Collaboration is key to our blue and green ammonia journey
Nutrien is one of the world’s largest producers of low-carbon ammonia today, with up to 1 million tonnes of production capability. We’ve recently taken another step in this journey, by teaming up with the US Department of Energy (DOE) and other partners to explore flexible zero-carbon ammonia production, as part of our efforts to help the world transition to low-carbon fertilizers.
Nutrien is one of 15 organizations involved in the DOE-funded Renewable Energy to Fuels Through Utilization of Energy-Dense Liquids (REFUEL) integration and testing program, which is working to create a carbon-free process for creating ammonia. Led by RTI, the partners are working to develop a 1 metric tonne-per-day, low- and zero-carbon ammonia facility, and use the resulting ammonia for agriculture, electricity generation and/or as a fuel.
“We’re proud to be part of this project – there’s no doubt that collaboration is key to our blue and green ammonia journey,” says Raef Sully, Executive Vice President and CEO of Nitrogen and Phosphate at Nutrien. “The prospect of a small-to-medium-scale ammonia plant that is efficient, requires low capital and has no carbon footprint is very exciting.”
Nutrien’s primary contribution is ammonia expertise – our employees will be involved from design and engineering through to commissioning.
"We’re re-imagining ammonia production here – and this will provide a tremendous opportunity for the participating employees to lend their experience to the project and share their learnings with Nutrien," says Blake Adair, Senior Manager of Projects, Innovation and Product Development at Nutrien. "This design has the potential to deliver carbon-free crop nutrients and fuels, which is aligned with our sustainability goals."
Ammonia 101
Ammonia (NH3), is one of the world’s most important commodities. Annual global ammonia production is approximately 180 million tonnes, of which about 80 percent is used for fertilizers and the rest for various industrial uses and products. Nutrien is the third-largest ammonia producer in the world, with the capacity to produce about 7 million tonnes annually.
Pure ammonia contains no carbon, so when fully combusted, the only end products are nitrogen and water vapor. Combined with the fact that there are credible low/zero carbon pathways for ammonia production, there’s significant interest globally in using ammonia as a fuel. Blake shared insights about these efforts and other blue and green ammonia-related projects in this article, published recently in Fertilizer Focus.
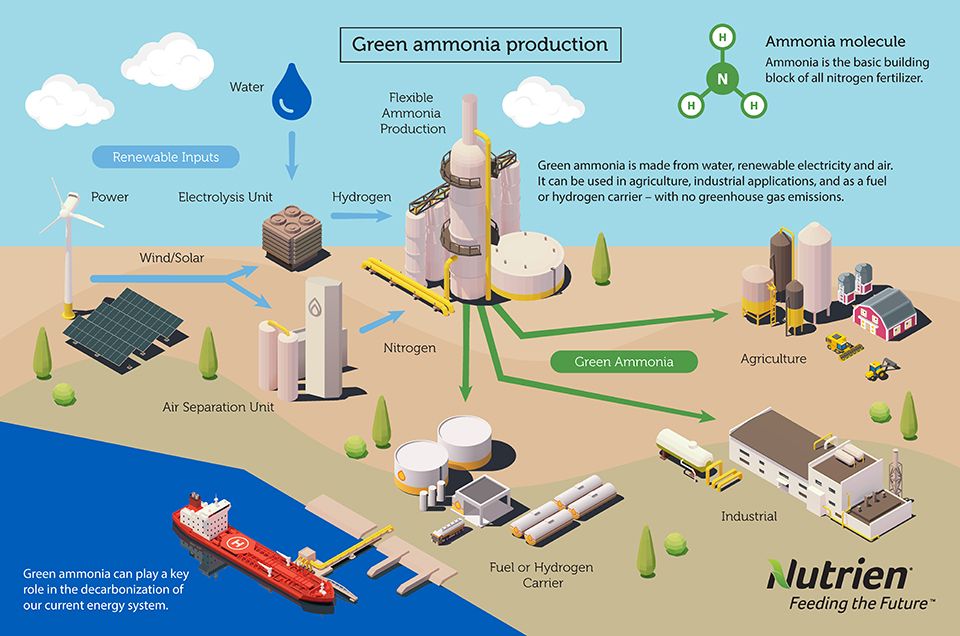
Meanwhile, development is underway around the world to take advantage of using ammonia as a hydrogen carrier. Hydrogen has the potential to play a key role in helping the planet achieve carbon neutrality, and ammonia – which is 17 percent hydrogen – has significant potential advantages when compared to other options to transport hydrogen.
What are Green and Blue Ammonia?
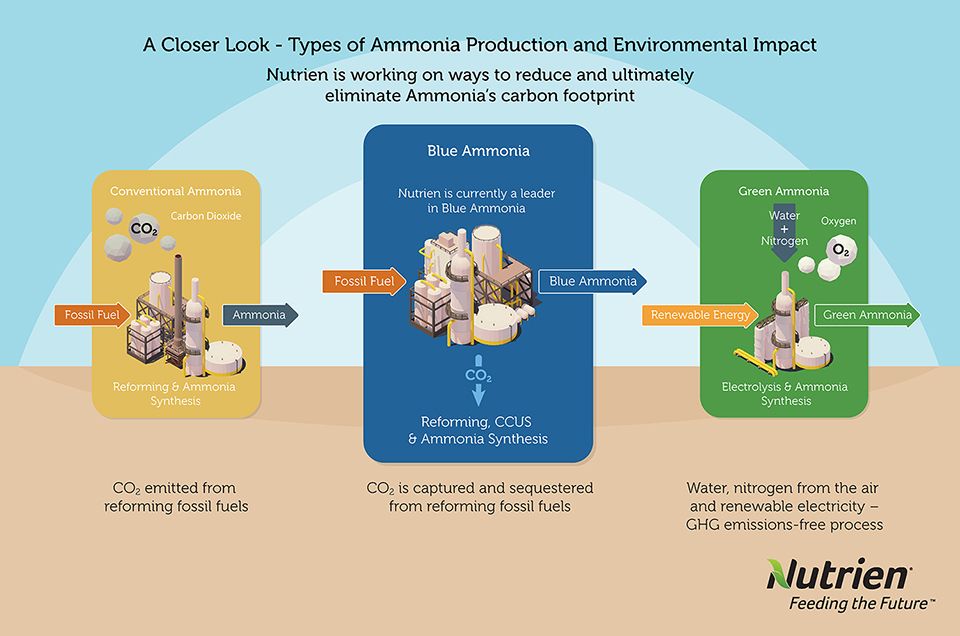
Conventional ammonia production using natural gas or coal generates a significant amount of carbon dioxide, so governments, agencies and companies, including Nutrien, are working on ways to reduce – and ultimately, eliminate – ammonia’s carbon footprint.
"Green" ammonia production – where the process of making ammonia is entirely renewable and carbon-free – is achieved by using renewable electricity and electrolysis to extract hydrogen from water. The hydrogen can then be combined with nitrogen from the air to make ammonia. The variable availability of renewable electricity like solar and wind make the consistent and large-scale production of green ammonia challenging with today’s technology – and that necessitates flexibility in a plant’s operation.
Low-carbon “blue” ammonia is produced by capturing carbon emissions during the production process and permanently sequestering them. Nutrien is one of the world's largest low-carbon ammonia producers today, with up to 1 million tonnes of production capability at our Redwater, Alberta; Geismar, Louisiana; and Joffre, Alberta operations.
Helping the world transition to low-carbon fertilizers, including blue and green ammonia, is one of the 2030 commitments in Nutrien’s Feeding the Future Plan.
Related stories


